PM Awas Yojana Faces Questions Amidst Allocation Scandals
Updated on : 16 January, 2025

Image Source: i.marketsmojo.com
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) is a flagship program designed to ensure affordable housing for all by offering financial assistance for home construction. Despite its noble intent, recent controversies have surfaced, with reports of irregular beneficiary selection, misuse of funds, and political interference, sparking concerns over the scheme's integrity and efficiency.
Introduction to PM Awas Yojana(PMAY)
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) is a transformative initiative by the Indian government aimed at providing affordable housing to millions of citizens, particularly from low-income and economically weaker sections. Launched with the vision of "Housing for All," it seeks to address the housing crisis in urban and rural areas across the country.
Overview of PM Awas Yojana:
PMAY is designed to facilitate the construction of affordable homes by offering financial assistance to individuals for building or purchasing homes. The scheme operates through two main components: PMAY (Urban) for urban areas and PMAY (Gramin) for rural areas. It provides subsidies on home loans, promotes the use of innovative building materials, and supports infrastructure development.
Importance of Affordable Housing in India:
Affordable housing is a critical need in India, where a significant portion of the population resides in informal settlements or overcrowded urban areas. The shortage of affordable homes limits economic mobility, quality of life, and access to basic amenities. PMAY plays a vital role in addressing this challenge, improving living conditions, and promoting inclusive urban development.
Historical Context and Evolution
India's housing policies have evolved over the decades, reflecting the growing need for affordable housing amidst rapid urbanization and population growth. In the early years post-independence, housing policies focused primarily on providing shelter to refugees and the urban poor. Over time, the government introduced various schemes like the "Slum Clearance Program" and the "Indira Awas Yojana" (IAY) aimed at addressing housing shortages in rural areas. However, these programs often lacked the scale and resources needed to meet the growing demand for affordable homes.
Inception of PM Awas Yojana
- The PMAY was launched on June 25, 2015, by Prime Minister Narendra Modi with the goal of ensuring "Housing for All" by 2022.
- The scheme aimed to provide affordable housing to the economically weaker sections, lower-income groups, and middle-income families, both in urban and rural areas.
- The initiative was built on the foundation of earlier housing policies but introduced a more comprehensive approach to tackle the housing shortage
Evolution and Milestones of the Scheme
Since its inception, PMAY has seen significant progress, with millions of homes sanctioned under the scheme. Key milestones include:
- 2015: Launch of PMAY, with an initial focus on urban areas.
- 2016: Expansion to rural areas under PMAY-Gramin, ensuring that homes were provided to the rural poor.
- 2017: The introduction of the "Credit Linked Subsidy Scheme" (CLSS) aimed at providing affordable loans to eligible beneficiaries.
- 2018-2020: Scaling up efforts with the construction of lakhs of homes and the introduction of new technologies for efficient and cost-effective housing construction.
- 2020: Adoption of the "Housing for All" vision under the "Atmanirbhar Bharat" initiative to further boost housing development across the country.
Popular Blogs
Objectives and Vision
Key Goals of PM Awas Yojana
The primary objective of PMAY is to provide affordable housing to all citizens, particularly low-income groups and economically weaker sections. Key goals include:
- Housing for All: Ensuring every citizen has access to safe and affordable housing.
- Subsidized Loans: Offering financial support through the Credit Linked Subsidy Scheme (CLSS) to make homeownership more accessible.
- Slum Rehabilitation: Redeveloping slums and providing better housing options.
- Infrastructure Development: Building essential services like roads, water, and sanitation alongside homes.
Vision for Urban and Rural Housing
PMAY aims to improve housing in both urban and rural areas:
- Urban Housing: Focuses on slum redevelopment and affordable housing in cities to accommodate the growing urban population.
- Rural Housing: Provides homes in rural areas to economically weaker families, improving their living standards and access to services.
Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
PMAY aligns with the UN�’s SDGs by:
- SDG 1 (No Poverty): Providing affordable housing helps reduce poverty.
- SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation): Ensures better access to water and sanitation in new housing projects.
- SDG 9 (Infrastructure): Promotes sustainable infrastructure and innovation in construction.
- SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities): Creates safer, more resilient cities with affordable housing.
- SDG 13 (Climate Action): Encourages eco-friendly construction practices.
Key Features of the Scheme
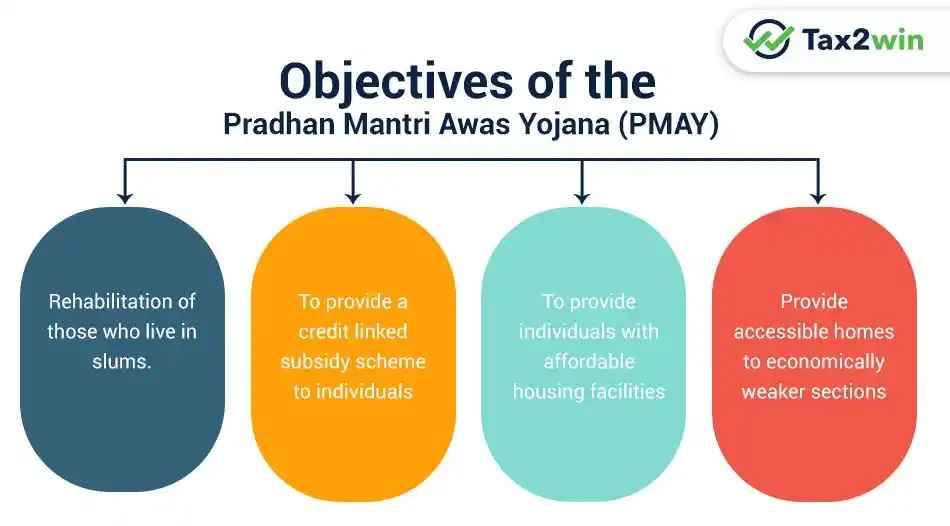
Image Source: Moneycontrol
Types of Housing Solutions Offered (Urban & Rural)
- Urban Housing: Focuses on slum redevelopment and affordable housing for low-income groups in cities.
- Rural Housing: Provides financial support to low-income families in rural areas for building or improving homes.
Financial Assistance and Subsidies
- Credit Linked Subsidy Scheme (CLSS): Offers interest subsidies on home loans for EWS, LIG, and MIG groups to make homeownership affordable.
- Slum Redevelopment: Financial assistance for redeveloping slums and providing new homes for residents.
Technology-Driven Approaches
- Innovative Construction: Uses eco-friendly materials and technologies to reduce costs and improve durability.
- Geospatial Mapping: Helps in planning and ensuring proper resource allocation.
- PMAY App and Portal: Provides easy access for beneficiaries to apply, track their status, and receive updates.
These features ensure that PMAY provides affordable, quality housing while using technology to enhance efficiency and transparency.
Eligibility and Beneficiary Criteria
Parameters for Urban Beneficiaries
Income Limits:
- Economically Weaker Section(EWS): Income up to ₹3 lakh
- Low Income Group(LIG): Income between ₹3 lakh and ₹6 lakh
- Middle Income Group(MIG): Income between ₹6 lakh and ₹18 lakh
- Land Ownership: Must have land to build a house.
- Slum Dwellers: Preference for in-situ rehabilitation.
Parameters for Rural Beneficiaries
- Income Limit: Families with income up to ₹3 lakh.
- Housing Status: Must not own a pucca house.
- Preference: Given to widows, the elderly, and disabled individuals.
Application and Approval Process
- Apply Online: Through the PMAY website or app.
- Document Submission: Submit income proof, land details, and identity proof.
- Verification: Applications are verified based on eligibility criteria.
- Approval and Subsidy: Approved beneficiaries receive subsidies under CLSS.
- Fund Allocation: Funds are sanctioned for construction or slum redevelopment.
| Criteria | Urban Beneficiaries | Rural Beneficiaries | Application Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Income Limits | EWS: ₹3 Lakh, LIG: ₹3-6 Lakh, MIG: ₹6-18 Lakh | Up to ₹3 Lakh | Apply online via PMAY website/app |
| Land Ownership | Required for new house | Not necessary | Submit documents: income, land, identity proof |
| Slum Dwellers | Preference for redevelopment | Not applicable | Application verified based on criteria |
| Housing Status | Must not own pucca house | Must not own pucca house | Subsidies given to approved applicants |
| Preference | First-time buyers | Widows, elderly, disabled | Funds for construction or slum rehab |
Achievements and Impact

Image Source: Moneycontrol
Success Stories and Transformational Case Studies
PMAY has positively impacted millions of houses under the PM Awas yojana, providing safe and affordable housing in both urban and rural areas. PMAY has transformed the lives of countless families across India by providing them with affordable homes. Success stories include:
- Slum Redevelopment: Communities in cities have been relocated to better housing, improving living conditions.
- Homeownership for Low-Income Families: Many families now own homes thanks to government subsidies.
Contributions to Urban Housing Development
PMAY has played a key role in urban housing:
- Affordable Housing Projects: Large-scale projects have reduced housing shortages in cities.
- Slum-Free Cities: Several cities have seen slums redeveloped into proper housing with amenities.
Rural Housing Achievements and Impact
In rural areas, PMAY has:
- Provided Homes: It has helped many rural families with new homes and better living conditions.
- Empowered Women: Homes are often registered in women's names, promoting gender equality.
Notable Projects Under PMAY
Several significant projects under PMAY have set benchmarks for housing development:
- In-Situ Slum Redevelopment Projects: Transforming existing slums into well-built housing complexes.
- Affordable Housing in Metro Cities: Large-scale construction projects in metro cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Bengaluru aim to cater to low-income groups.
- Rural Housing Projects: Focused on building homes in rural areas, bringing significant improvements in infrastructure and sanitation.
Recent Issues and Challenges
In 2025, PM Awas Yojana (PMAY), which aims to provide affordable housing for millions, is facing significant backlash due to growing controversies.
Allegations of Corruption in Allocation
- PMAY's distribution process is under fire as reports of favoritism and corruption emerge.
- Critics claim that political influence and under-the-table deals are steering the allocation of homes, leaving eligible beneficiaries in the lurch.
- Many families who meet the scheme’s criteria are still waiting for homes, while others with questionable eligibility have been prioritized.
Inequitable Distribution of Housing
- Another major issue is the uneven distribution of homes. In urban and rural areas alike, several deserving families are reportedly being left out of the scheme.
- Some even accuse officials of misusing funds meant for construction, further widening the gap between demand and supply.
Delays and Unfinished Projects
- Beneficiaries are expressing frustration over long delays in home construction. Many have yet to receive the promised houses, with some forced to live in unsafe or temporary conditions.
- Even once completed, homes are often handed over with incomplete infrastructure, leaving residents to deal with issues like poor water supply and sanitation.
Quality Concerns and Public Outcry
- Beyond delays, there are growing concerns about the quality of homes built under PMAY.
- Multiple complaints have surfaced about substandard construction, with homes reportedly built using low-quality materials.
- Beneficiaries are questioning the scheme's commitment to providing safe and durable housing.
These controversies are casting a shadow over the success of PMAY, raising serious questions about its implementation, fairness, and long-term effectiveness in addressing India’s housing crisis.
Policy and Implementation Updates of 2025
In 2025, the government introduced significant policy updates and new initiatives to address the challenges faced by PM Awas Yojana (PMAY) and improve its effectiveness.

Image Source: Moneycontrol
To streamline and improve PMAY's outreach, the government has made key policy adjustments:
- Expansion of Beneficiary Criteria: The eligibility criteria have been broadened to include more marginalized groups, especially in rural areas, to ensure that those truly in need benefit from the scheme
- Increase in Budget Allocation: A significant increase in funding has been allocated to PMAY, allowing for the construction of more affordable homes and improved infrastructure in rural and urban areas.
- Focus on Transparent Allocation: The government has introduced stricter monitoring and auditing processes to curb corruption and ensure homes are allocated to eligible beneficiaries based on need, not influence.
In response to ongoing criticisms, the government has launched several initiatives aimed at improving the scheme's impact:
- Fast-Track Approval Process: A new fast-track approval system for subsidy disbursements has been introduced to speed up the construction process and reduce delays.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): The government is encouraging collaboration with private developers to accelerate construction, leveraging their expertise and resources to meet growing demand.
- Technology Integration: A digital platform has been set up to track real-time project progress and beneficiary data, ensuring transparency and efficient execution.
To address the ongoing issues faced by PMAY beneficiaries, several measures have been implemented:
- Quality Control Guidelines: Strict quality control measures have been enforced to ensure that the construction of homes meets the required standards, with inspections at every phase of development.
- Enhanced Support for Maintenance: The government has introduced a new support program for the maintenance of homes, providing financial assistance for repairs and upkeep, particularly in rural areas.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Awareness campaigns are being rolled out to educate beneficiaries on the application process and ensure they are aware of their rights under the scheme.
Future Prospects
As India continues to develop and urbanize, the future of PM Awas Yojana (PMAY) holds significant promise, with several trends and potential changes on the horizon.
Predictions for the Next Five Years
Over the next five years, PMAY is expected to witness a rapid expansion, with the government aiming to meet its goal of providing affordable housing to millions more citizens. By 2030, it is projected that urban housing shortages will be significantly reduced, and rural areas will see substantial improvements in living conditions. Increased funding and better project execution are expected to accelerate this growth.
Potential Changes to Improve Accessibility and Impact
In the coming years, there are several potential changes aimed at improving the accessibility of PMAY, including:
- Simplification of Application Process: The government may implement a more user-friendly and accessible application process, particularly through mobile applications, to increase participation.
- Focus on Inclusive Housing: With a shift towards more inclusive policies, there may be more targeted efforts to ensure that marginalized and vulnerable groups are better served by the scheme.
Conclusion
In the coming years, PM Awas Yojana (PMAY) is set to expand its reach, aiming to address India's housing needs more effectively. Simplified application processes and inclusive policies will enhance accessibility for marginalized groups. Technology will play a pivotal role in improving transparency and speeding up approvals, while innovations in construction methods will reduce costs and delivery times. The government's focus on quality control and support for maintenance will ensure that the homes built under the scheme remain sustainable. Overall, PMAY’s future prospects are bright, with substantial improvements expected in both urban and rural housing sectors.