55th GST Council Meeting: Key Agenda, Highlights, and Economic Impacts
Updated on : 21 December, 2024

Image Source: pbs.twimg.com
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council plays a pivotal role in shaping India’s indirect tax landscape. As a constitutional body, it serves as a bridge between the central and state governments, ensuring effective coordination and implementation of GST across the nation. The upcoming 55th GST Council meeting, scheduled for December 21, 2024, in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, is highly anticipated due to its potential to address significant tax reforms and policy changes. This blog will delve into the objectives and agenda of the meeting while providing insights into the functioning of the GST Council.
What is the GST Council?
The GST Council is a constitutional body established under Article 279A of the Indian Constitution, responsible for overseeing the Goods and Services Tax (GST) framework in India. It is chaired by the Union Finance Minister and includes finance ministers from all states and union territories. The council's primary role is to make recommendations to both central and state governments regarding GST-related issues, including tax rates, exemptions, and compliance requirements. It aims to ensure a uniform tax structure across the country, facilitating discussions and decisions that impact India's indirect tax regime.
Significance of the 55th Meeting
The significance of the 55th GST Council meeting lies in its potential impact on various sectors of the economy. Key discussions are expected around rate rationalization, adjustments in tax slabs, and addressing long-standing issues such as the inverted duty structure. The decisions made during this meeting could influence consumer prices, business operations, and overall economic growth.
How often does the GST Council meet?

Image Source: cleartax.in
The GST Council is required to meet at least once every three months, which translates to a minimum of four meetings per year. However, additional meetings may be convened as necessary to address urgent issues or emerging challenges within the tax regime. These meetings are essential for evaluating the effectiveness of existing policies and making timely adjustments to ensure smooth functioning of the GST system. The frequency of meetings can vary based on the needs and circumstances, with some meetings occurring more frequently than the minimum requirement.
Agenda Highlights

Image Source: rmpsco.com
The 55th GST Council meeting, scheduled for December 21, 2024, in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, has an extensive agenda focusing on several critical issues:
Key Issues to be Discussed
- Rate Rationalization: Proposed changes to GST rates for various goods and services, including potential reductions for life and health insurance premiums and increases for luxury items.
- Inverted Duty Structure: Review of challenges related to input tax credits, particularly where input goods are taxed at higher rates than finished products.
- Aviation Turbine Fuel (ATF): Consideration of including ATF under the GST framework to standardize taxation and allow airlines to claim input tax credits.
- Compensation Cess: Review of future cess rates and their implications for revenue generation and state finances.
Summary of Previous Meetings
In prior meetings, the GST Council made significant decisions regarding tax rates on essential goods and exemptions for specific sectors. The focus has consistently been on simplifying the tax structure while ensuring adequate revenue generation for both central and state governments. The council's efforts aim to enhance compliance and address the needs of various stakeholders within India's economy.
Rate Rationalization
The upcoming 55th GST Council meeting will focus significantly on rate rationalization, aiming to streamline GST rates across various categories of goods and services.
Proposed Changes to GST Rates
- Reductions on Essential Goods
- Health Insurance: There are proposals to reduce the GST rate on health insurance premiums, potentially exempting term life insurance from GST entirely. This aims to enhance affordability for consumers, especially for those with lower coverage amounts.
- Food Delivery Services: The council may also consider lowering the GST rate on food delivery platforms like Swiggy and Zomato from 18% to 5%, without allowing input tax credits. This change is intended to make food delivery more accessible.
- Increases on Luxury Items
- Luxury Goods: Conversely, there could be proposed increases in GST rates for luxury items, such as high-end watches and designer apparel. This adjustment seeks to ensure that luxury consumption contributes adequately to government revenues, with discussions suggesting a potential new slab of 35% for 'sin' goods like tobacco and aerated beverages.
Discussion on Merging Tax Slabs
The council is expected to discuss the possibility of merging multiple tax slabs into fewer categories. This move aims to simplify compliance for businesses and reduce administrative burdens, addressing the ongoing criticism regarding the complexity of the current GST structure, which includes four primary rates: 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%.
Inverted Duty Structure
The inverted duty structure is a significant issue affecting various sectors under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime.
Overview of Current Issues
In an inverted duty structure, the tax rate on inputs is higher than that on finished goods. This situation leads to businesses accumulating input tax credits (ITC) that they cannot effectively utilize, creating cash flow challenges. For instance, a manufacturer might pay 18% GST on raw materials but only charge 5% GST on the final product, resulting in excess ITC that remains unutilized and blocked in their accounts.
Proposed Corrections for Various Sectors
To address this imbalance, proposals are likely to focus on adjusting GST rates so that raw materials attract lower taxes compared to finished products. This adjustment aims to improve cash flow for manufacturers, particularly in sectors like textiles and leather, where the inverted duty structure has been particularly detrimental. By aligning input and output tax rates more closely, the government seeks to enhance operational efficiency and reduce the compliance burden on businesses.
Aviation Turbine Fuel (ATF) Inclusion

Image Source: businessindia.co
A significant agenda item for the upcoming 55th GST Council meeting is the inclusion of Aviation Turbine Fuel (ATF) under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime. Currently, ATF is taxed through central excise duty and state VAT, which creates inefficiencies in the tax structure.
- Current Tax Structure: ATF is subject to an 11% central excise duty and varying VAT rates, which can reach as high as 30% in some states. This multi-layered taxation leads to cascading taxes (tax on tax), increasing the effective cost of ATF for airlines. Additionally, since ATF is excluded from the GST framework, manufacturers cannot claim input tax credits (ITC) on the GST paid for inputs used in ATF production, further straining their finances.
- Potential Benefits of Inclusion: Incorporating ATF into the GST framework would allow airlines to claim ITC, potentially reducing operational costs significantly. This change could enhance operational efficiency within the aviation sector and promote uniformity in taxation across states. The move has been a long-standing demand from the aviation industry, which argues that it would alleviate the financial burden caused by high ATF prices.
Compensation Cess Review
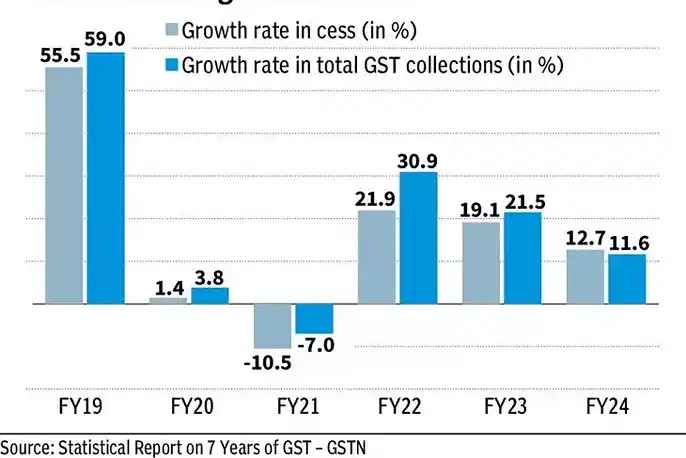
Image Source: thehindubusinessline.com
The Compensation Cess Review is a critical agenda item for the upcoming GST Council meeting, focusing on the future of the compensation cess originally introduced to compensate states for revenue losses due to the implementation of GST.
Future of Compensation Cess Rates
The council will review the current cess rates and may discuss extending them beyond their initial timeline, which is set to end in January 2026. This extension is considered necessary to ensure that states continue receiving adequate compensation, especially as they have expressed reluctance to lose this revenue stream. Projections indicate that approximately ₹20,000 crore could be collected via the GST compensation cess by February 2026, and discussions will likely revolve around how to manage any surplus generated after loan repayments are completed.
Special Rates for Sin Goods
Additionally, the council may consider implementing higher cess rates on sin goods such as tobacco products and aerated drinks. This approach serves a dual purpose: discouraging consumption of these products while generating additional revenue. The idea is to align taxation with public health objectives and maximize revenue collection from sectors that are typically associated with higher social costs.
Overall, the discussions will center on how to effectively manage the compensation cess in light of changing economic conditions and state needs, ensuring that any future framework remains sustainable and equitable.
Recommendations from the Group of Ministers (GoM)

Image Source: x.com
The Group of Ministers (GoM) plays a crucial role in formulating recommendations for the GST Council's consideration, particularly regarding rate rationalization and compliance issues.
Summary of GoM Findings
The GoM has identified key areas requiring attention, including necessary rate adjustments across multiple categories based on current market conditions and revenue needs. Their findings emphasize the importance of balancing affordability for consumers with the need for adequate revenue generation for state and central governments.
Key Recommendations on Rate Changes
The GoM's recommendations are expected to focus on strategic rate changes, such as increasing GST on sin goods like tobacco and aerated drinks to 35% from the current 28%. Additionally, they propose rationalizing rates for apparel, suggesting tiered rates based on the price of garments.
The overall goal is to simplify the tax structure while ensuring that essential goods remain affordable and that luxury consumption adequately contributes to government revenues.
Sector-Specific Impacts
Decisions made during the upcoming GST Council meeting will have varied impacts across different sectors:
| Sector | Expected Changes | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | - Proposed reduction in GST rates on health insurance premiums. - Exemption for term life insurance policies. | Increased affordability and access to health insurance for consumers. |
| Aviation | - Inclusion of Aviation Turbine Fuel (ATF) under GST. - Potential for lower operational costs for airlines. | Enhanced financial viability for airlines, potentially leading to lower ticket prices. |
| Luxury Goods | - Increase in GST rates on high-end watches (from 18% to 28%). - Increase on shoes priced above ₹15,000 (from 18% to 28%). | Shift in consumer purchasing behavior; potential decrease in demand for luxury items. |
| Essential Goods | - Reduction in GST rates on food delivery services (from 18% to 5%). | Lower costs for consumers, making essential services more accessible. |
| Sin Goods | - Proposed special rate of 35% on items like tobacco and aerated drinks. | Discouragement of consumption of harmful goods while generating additional revenue. |
| Textiles and Apparel | - Proposed changes in GST rates for readymade garments: - 5% for items costing up to ₹1,500. - 18% for items between ₹1,500 and ₹10,000. | Improved clarity and potential benefits for consumers shopping for clothing essentials. |
| Food Delivery Services | - Reduction in GST rates to make services more affordable. | Increased usage of food delivery platforms, benefiting both consumers and service providers. |
Conclusion
The upcoming 55th GST Council meeting represents a critical juncture in India's taxation landscape. With significant discussions planned around rate rationalization, sector-specific impacts, and long-standing issues like the inverted duty structure, stakeholders from various sectors will be keenly observing outcomes that could shape economic policies moving forward. As India continues to navigate its post-pandemic recovery phase, effective decision-making during this meeting will be crucial in supporting growth while ensuring fairness in taxation across all segments of society. This blog provides a comprehensive overview of what can be expected from the upcoming GST Council meeting while highlighting its importance within India's economic framework. Each section aims to inform readers about key issues at play while fostering a deeper understanding of how these decisions affect everyday life in India.