GRAP 4 Restrictions in Delhi-NCR: What's Open and Shut?
Updated on : 17 December, 2024

Image Source: Adobe Stock
Delhi-NCR (National Capital Region) is grappling with a severe air pollution crisis, leading to the reimposition of Stage-IV restrictions under the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP). The Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) announced these measures after pollution levels surged into the 'severe' category, with the Air Quality Index (AQI) exceeding 400.

Image Source: Hindustan Times
What is GRAP?
GRAP stands for Graded Response Action Plan, which is a framework established by the Indian government to manage air pollution in Delhi and its surrounding areas. The plan consists of four stages:
-
Stage 1: For moderate pollution (AQI 201-300).
-
Stage 2: For poor air quality (AQI 301-400).
-
Stage 3: For very poor air quality (AQI 401-450).
-
Stage 4: For severe air quality (AQI above 450).
Why Were Grap 4 Restrictions Imposed?

Image Source: The Hindu
The CAQM reimposed Stage-IV restrictions on December 16, 2024, after the AQI in Delhi-NCR rose to alarming levels. On that day, the AQI was recorded at 367 at 2 PM and 351 at 9 AM, indicating a sharp decline in air quality due to unfavorable meteorological conditions such as calm winds and low mixing heights. By later in the day, the AQI had crossed the threshold of 400, prompting immediate action.
Key Restrictions Under Grap 4
- Construction Activities

Image Source: Adobe Stock
What’s Allowed:
- Essential construction work related to public projects like hospitals and railways may continue.
What’s Not Allowed:
- All other construction activities are completely banned. This includes residential buildings, commercial projects, and any demolition work.
- The ban on construction and demolition (C&D) activities under GRAP Stage III has been extended to linear public projects, including highways, roads, flyovers, power transmission lines, pipelines, and telecommunication infrastructure.
- Industrial Operations

Image Source: Adobe Stock
What’s Allowed:
- Industries that use cleaner fuels like natural gas can operate under strict monitoring.
What’s Not Allowed:
- Industries that use coal or other high-polluting fuels must stop operations.
- Non-essential industries are required to halt production until air quality improves.
- Vehicle Restrictions

Image Source: Indian Express
What’s Allowed:
- Emergency vehicles (like ambulances) can operate without restrictions.
- Public transport services such as buses and metro trains continue to function normally.
- Trucks carrying essential goods or services are allowed entry into Delhi.
- Vehicles operating on LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas), CNG (Compressed Natural Gas), electric vehicles, or BS-VI diesel are permitted.
What’s Not Allowed:
- All types of trucks are banned from entering Delhi unless they are carrying essential goods or services.
- Diesel vehicles registered in Delhi that are BS-IV and older heavy goods vehicles (HGVs) are banned unless they are engaged in essential services or transporting essential commodities.
- School Operations
What’s Allowed:
- Schools can conduct classes in hybrid mode (both online and offline) for students in Classes VI to IX and XI in Delhi and districts such as Gurugram, Faridabad, Ghaziabad, and Gautam Buddh Nagar where online options are feasible. The choice of online mode is left to students and their guardians.
What’s Not Allowed:
- In-person classes for younger students (up to grade 5) have shifted to online learning.
- Other districts in NCR are encouraged to adopt hybrid learning for schools based on feasibility.
- Public and Private Offices
What’s Allowed:
- Government offices can operate with only 50% of their staff on-site.
What’s Not Allowed:
- Non-essential businesses may be asked to close depending on the situation.
- Public, municipal, and private offices in NCR must function at 50% on-site capacity, with the remaining employees working from home.
- The Central Government is advised to consider work-from-home options for employees in central government offices.
- Outdoor Activities
What’s Allowed:
- Parks and open spaces remain accessible for exercise and walking, but people are advised to limit their time outdoors.
What’s Not Allowed:
-Outdoor sports events and large gatherings are discouraged due to poor air quality.
What Stays Open?
- Essential Services:
- Grocery stores
- Pharmacies
- Hospitals
- Emergency services
- Public Transport:
- Metro services continue to operate but may have limited capacity due to social distancing protocols.
- Online Education Platforms:
- Schools utilizing online platforms for hybrid learning remain functional.
- Work-from-Home Arrangements:
- Employees working remotely can continue their jobs without interruption.
Impacts on Daily Life
Commuting Challenges
With restrictions on private vehicles and heavy trucks, commuting will be affected significantly. Residents may need to rely more on public transport, which could lead to overcrowding on buses and metro trains.
Possible Solutions:
To address these challenges, authorities may implement additional services or increase the frequency of buses during peak hours. Carpooling initiatives could also be promoted to reduce the number of vehicles on the road.
Economic Consequences
The ban on construction activities and limitations on various industries may lead to economic repercussions. Delays in projects could result in financial losses for contractors and workers alike.
Long-Term Effects:
The long-term effects could include job losses in construction and related sectors if restrictions persist for an extended period. Small businesses may also struggle due to reduced foot traffic and customer access.
Health Implications
Poor air quality poses serious health risks. Residents are advised to limit outdoor activities, especially vulnerable populations such as children and elderly individuals.
Health Precautions:
To mitigate health risks, individuals should consider wearing masks when going outside, using air purifiers at home, and staying indoors during peak pollution hours (typically early morning and late evening).
Government Initiatives and Support
To help those affected by these restrictions, the government has announced several initiatives:
-
Financial Assistance for Affected Workers: Support programs for workers impacted by halted construction activities or industry closures.
-
Enhanced Public Transport Services: Increasing the frequency of buses and metro trains to accommodate more passengers.
-
Awareness Campaigns: Educating residents about air quality issues and encouraging practices that can help reduce pollution at an individual level.
-
Health Monitoring Programs: Establishing health camps in areas severely affected by pollution to monitor residents' health conditions related to air quality.
-
Collaboration with NGOs: Partnering with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) for community outreach programs focused on environmental awareness and pollution reduction strategies.
Public Health Recommendations
Community involvement is essential in combating air pollution during Grap 4 restrictions:
-
Local Initiatives: Residents can engage in local initiatives aimed at reducing pollution—such as tree planting drives or community clean-up events.
-
Advocacy for Policy Changes: Community groups can advocate for long-term policy changes that address the root causes of air pollution—such as stricter emissions regulations for vehicles and industries.
-
Educational Workshops: Organizing workshops in neighborhoods about sustainable practices like composting, recycling, and using public transport can foster a culture of environmental responsibility.
-
Social Media Campaigns: Utilizing social media platforms to spread awareness about air quality issues can engage more people in discussions about solutions.
The Role of Technology in Managing Air Quality
Technology plays a crucial role in monitoring and managing air quality:
- Air Quality Monitoring Systems: The government has set up various monitoring stations across Delhi-NCR that provide real-time data on air quality levels. This data helps authorities make informed decisions regarding GRAP implementation.
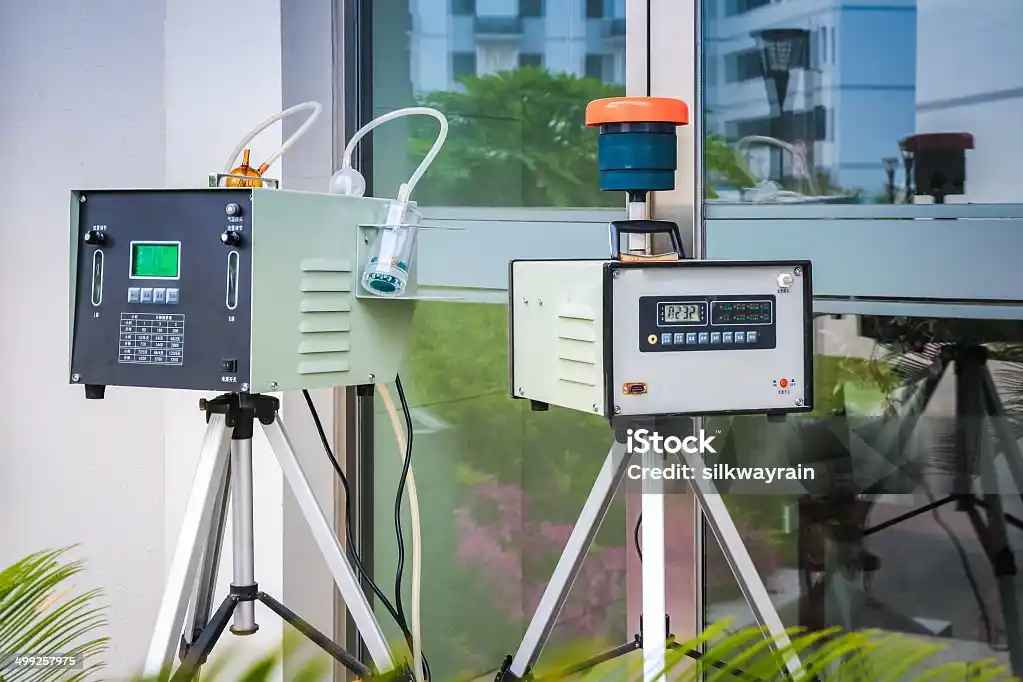

Image Source: istock
- Mobile Applications: Several mobile apps allow residents to check AQI levels before heading outdoors, helping them plan their activities accordingly.
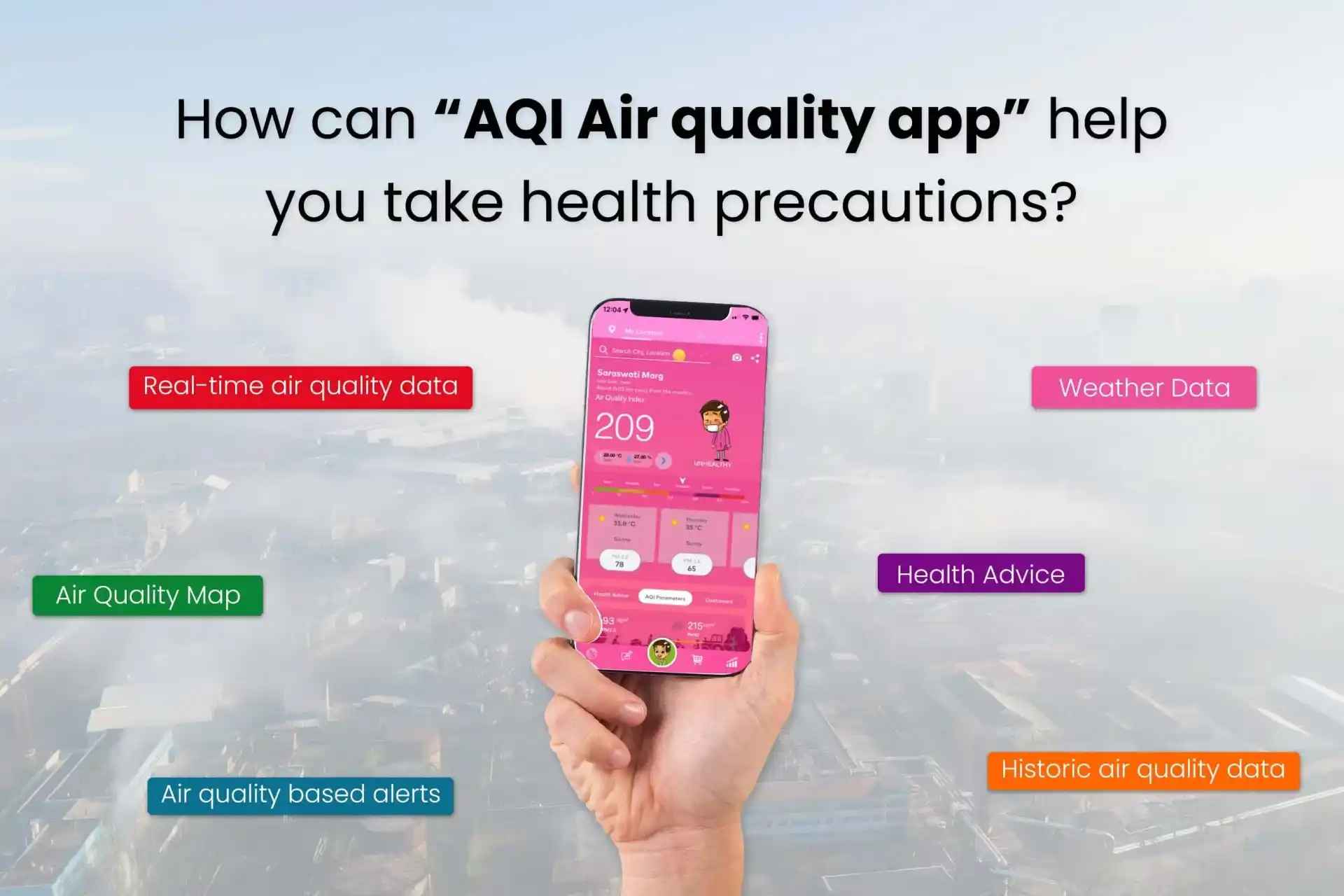
Image Source: Pranaair.com
-
Smart Traffic Management: Implementing smart traffic management systems can help reduce congestion on roads, thereby lowering vehicle emissions during peak hours.
-
Renewable Energy Solutions: Encouraging the use of renewable energy sources like solar power can significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels that contribute to air pollution.

Image Source: istock
Long-Term Solutions for Air Quality Improvement
While Grap 4 restrictions aim to provide immediate relief from severe pollution levels, long-term solutions are necessary for sustainable improvement:
-
Promoting Electric Vehicles (EVs): Encouraging the use of electric vehicles through subsidies or tax incentives can help reduce vehicular emissions significantly.
-
Improving Public Transport Infrastructure: Investing in better public transport systems will encourage more people to use buses or trains instead of personal vehicles.
-
Implementing Green Building Codes: Mandating green building practices can reduce emissions from construction activities while promoting energy efficiency.
-
Encouraging Sustainable Agricultural Practices: Farmers should be educated about alternative methods of crop management that do not involve burning stubble, such as composting or using bio-decomposers.
-
Strengthening Policies Against Industrial Pollution: Stricter regulations on industries regarding emissions standards can lead to cleaner production processes over time.
Conclusion
The Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) Stage IV represents a critical step towards addressing severe air pollution challenges faced by Delhi-NCR. While immediate measures such as vehicle restrictions and construction bans aim to mitigate health risks associated with poor air quality, it is essential for stakeholders at all levels—government bodies, industries, communities—to collaborate on long-term strategies that ensure sustainable improvements.